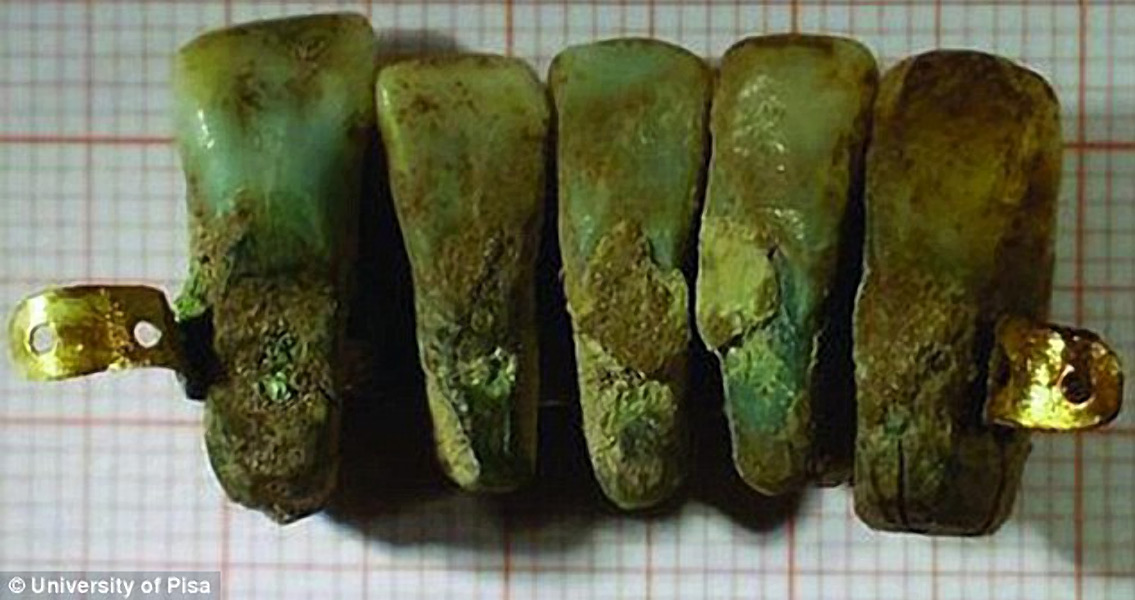
<![CDATA[Archaeologists working at a monastery located in Lucca, Tuscany, in central Italy have discovered a unique set of 400-year-old dentures. The team of paleopathologists with the University of Pisa, whose specialty is historical disease, discovered the dental prosthesis in an ancient family tomb. Scientist theorize that the dentures date to between the latter half of the fourteenth century and the first half of the seventeenth century, making them the oldest recorded set of false teeth in existence. Dentures constructed using both animal and human teeth are known to have been produced by the Etruscans and Romans as far back as 7 BCE. The first dentures made of porcelain arrived in the late eighteenth century, before then other sources such as ivory, animal teeth, bone, human teeth and other strong materials were used. Dr. Simona Minozzi, a member of the team, told The Local: "Although there are descriptions of similar objects in texts from the period, there is no known archaeological evidence. The dentures found in the tomb are the first example of dentures from this historical period, and as such are a valuable addition to the history of dentistry." The Etruscan people were the first to take a more artistic approach to basic work in the mouth. Considered to be highly intelligent, the Etruscan’s constantly sought out ways to increase their knowledge. Their appearance was important to them and they consistently tested medical boundaries to improve their looks. What knowledge they had of dentistry they picked up during their travels – filling gold teeth was one of their first experiments. In one well-preserved mouth, gold bands were found, wrapped around the teeth and then cemented to them by soldering. The procedure was done around 700 BCE and is the first known instance of mouth prosthetics being used. The dental device discovered in Lucca is made up of five teeth: two lateral canines and three central incisors which were covered with a layer of metal and incorrectly aligned. CT scanning of the teeth determined their metal coating was primarily gold, with smaller amounts of silver and other metals. Additionally, a layer of tartar was found on the surface indicating that the dentures had been worn for a substantial time. The team members believe that each tooth originally belonged to a different person, and that they were connected to each other and also the lower gums of the person wearing them. The teeth were discovered inside a tomb where generations of Guinigis were buried one on top of another. The Guinigis were a group of aristocratic and powerful traders and bankers that governed the city. Researchers have been conducting excavations at the site in order to study the remains of over 200 skeletons buried inside a San Francesco convent chapel. A Roman Catholic church and monastery constructed in the Gothic style is located inside the historic quarters of Lucca. Today, the structure is divided into three sections: cloisters, a courtyard and a green space. Completely renovated, the building is used for large events, public lectures and seminars. ]]>
Early Set of Dentures Constructed With Human Teeth